(Explaining the Schedule M1 for Dummies)
So you’re a small business owner and you just got your business return back. You take a look at the tax return and it says your net income is $20,000 but you gave your QuickBooks profit and loss statement to your account and it said that your income was $15,000. What happened? Maybe instead it was the other way and your tax income was lower. What’s up with that?
Well first thing, if you have an accountant doing your taxes, she should be able to explain exactly what’s going on. (If she can’t, it’s time for a new accountant.) But the simple answer is right on your tax return. It’s called the Schedule M1. If you’ve got a corporation, it will be on page 5 of the tax return. If you’ve got a partnership, it’s on page 4, right underneath the balance sheet.
Schedule M1 is the part of the tax return that explains what’s different between the books that you handed your accountant and the tax return that you’re giving to the IRS. If you had less than $250,000 in revenue, you don’t need to submit an M1 to the IRS (tax programs will leave them blank), but it’s still a good idea to complete those schedules to make sure your books are straight.
So what are the most common discrepancies between tax and book income? That’s easy; you’ll find it in the meals and entertainment category and depreciation. If you don’t have expenses in either of these categories, most likely your tax income and book income are going to match up just fine. But if you do have meals and entertainment or depreciation, they almost always affect your tax income.
Let me explain the meals and entertainment first. That’s the category where the IRS only allows you to claim a 50% deduction on there. So let’s say you spent $3,000 in meals and entertainment. On your tax return, you’d only get to expense $1,500. That means there’s another $1500 expense that’s recorded on your books that’s not on your tax return. So, in this example your tax net income is higher than your book income.
Depreciation usually goes the other way. Often small businesses ignore depreciation. Or they run depreciation through their software program, but it’s not the same depreciation schedule that’s used for taxes. For example, using the straight line method for book purposes but using the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) for tax purposes. Usually that makes for a tax adjustment the other way.
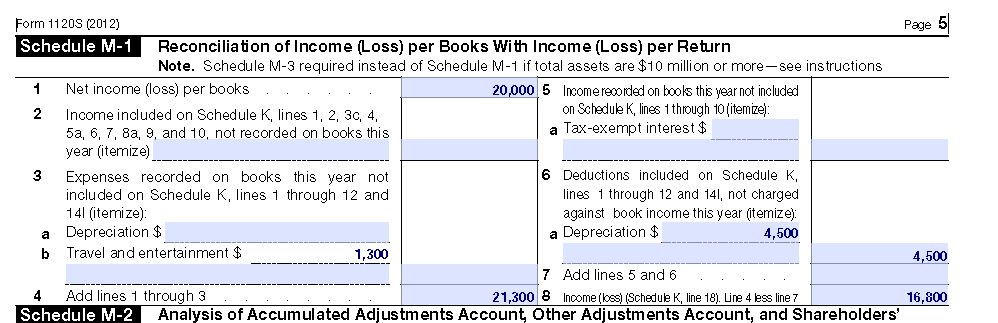
Let’s look at an example so you can see what the Schedule M-1 looks like and how it affects your net income. In the example below, the business owner showed $20,000 of net income on his QuickBooks profit and loss statement. He had $2,600 of travel and entertainment expenses, so half of that get’s added to his taxable income. He also had $4,500 of depreciation that showed up on his tax return, but he didn’t include in his QuickBooks, so that reduces his taxable income.
$20,000 (net income from the profit and loss statement) + $1300 (half of the meal and entertainment expense) – $4500 (the depreciation expense) = $16,800 (the net income shown on the tax return)
There are lots of other items that can affect the Schedule M1. These two are so common that many tax programs automatically plug them in for you. Another common item that might show up on the M-1 is when you’ve got an expense on your profit and loss statement that your accountant says, “No, you can’t count that on your tax return.” (We don’t do that to be mean, we just don’t look that good in prison orange.)
Why you want the Schedule M-1. Let’s say you file your business tax return and you get audited by the IRS. The first thing they do is ask for your profit and loss statement and your bank records. The examiner takes one look at your P&L and sees you have net income of $20,000—but you’re tax return says you made $16,800. He’s licking his chops because he gets to assess you additional taxes and he hasn’t even opened your bank statement yet. Aha! You’ve got your M1 showing the depreciation. Your butt is covered.
Now in real life, the IRS examiner would notice the depreciation eventually anyway. But sometimes there will be items in the M-1 that aren’t so obvious. That’s why you want this reconciliation, because by the time the IRS gets around to auditing your books, you’ll forget the little adjustments—unless they’re tracked. M-1 keeps you neat and tidy.